CombineDisplacement
Overview
CombineDisplacement is meant to handle one Displacement of both types: NormalDisplacement and VectorDisplacement. When combining two Displacements of the same type, use LayerMap or OpMap for the data that will connect to displacement.
This combination does not consider ordering for orientation; both inputs are displacing using the geometry normals.
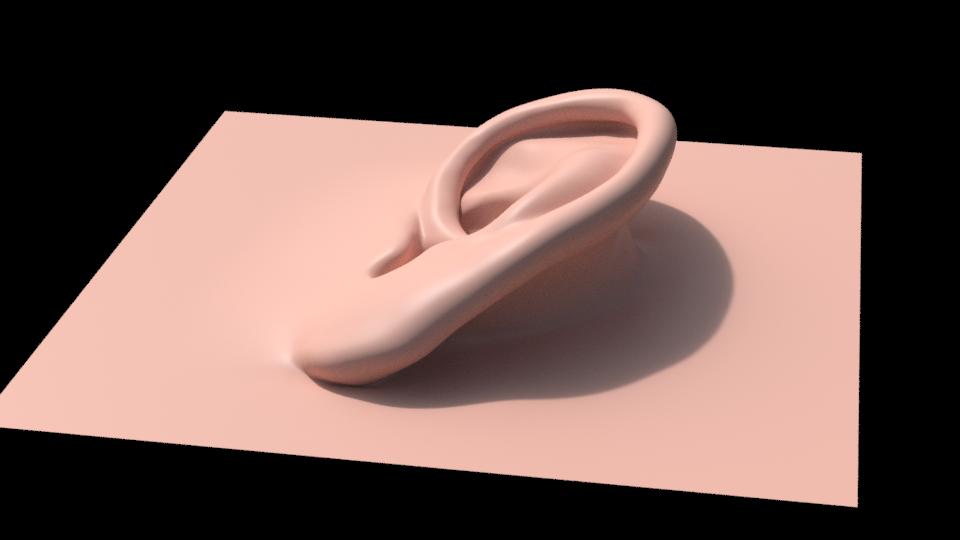
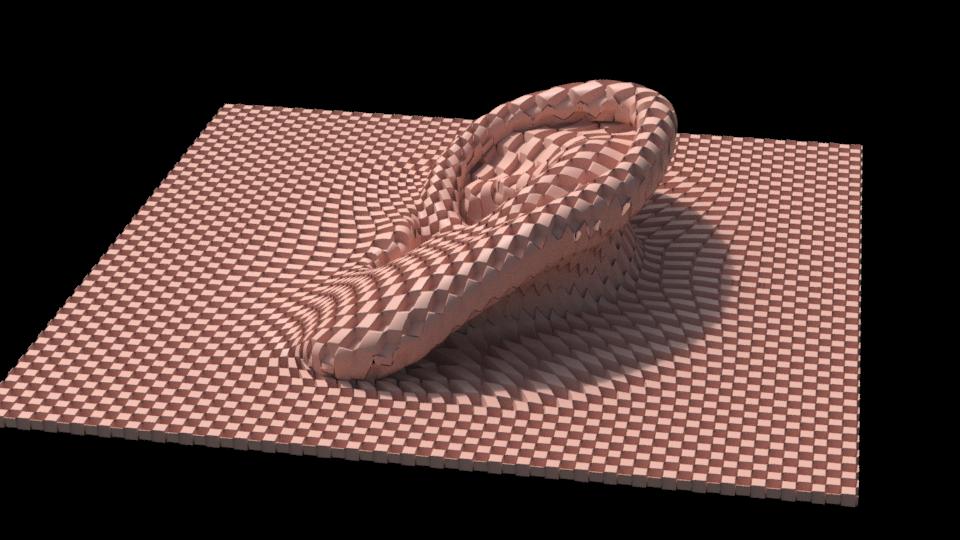
Attribute Reference
General attributes
bound_padding
Float
default: 0.0
bound padding defines how much to extend the bounding box of the object. Keep this value as low as possible unless the geometry skips tessellation because control cage bounding box is out of camera frustum but the displacement stretch out of the original object bounding box (pre-displacement). Setting the bound padding too large will consume more memory and tessellation time.
input_1
Displacement
default: None
Displacement object 1
input_2
Displacement
default: None
Displacement object 2
operation
Int enum
0 = “add” (default)
1 = “max magnitude”
2 = “min magnitude”
The method used for combining the displacements
scale_1
Float bindable
default: 1.0
Scale of input 1
scale_2
Float bindable
default: 1.0
Scale of input 2
Examples
local checkermap = CheckerboardMap("/Scene/surfacing/checkermap") {
}
local noiseWorley = NoiseWorleyMap("/Scene/surfacing/noiseWorley") {
["space"] = 2,
["scale"] = Vec3(0.05, 0.05, 0.05),
["use smoothstep"] = true,
}
local vDisplacement = VectorDisplacement("/Scene/surfacing/vDisplacement") {
["vector"] = bind(noiseWorley),
["factor"] = 1,
["source space"] = 1,
}
local nDisplacement = NormalDisplacement("/Scene/surfacing/nDisplacement") {
["height"] = bind(checkermap, 1),
}
-- note that inputs 1 and 2 are different types of displacement map
local combineDisplacement1 = CombineDisplacement("/Scene/surfacing/combineDisplacement1") {
["operation"] = 0,
["input 1"] = vDisplacement,
["scale 1"] = 10,
["input 2"] = nDisplacement,
["scale 2"] = bind(noiseWorley, 8),
}